Acupuncture Disadvantages: Myth vs. Reality in Healthcare
Acupuncture is indeed a timeless form of medicine that originated in China and has been around for thousands of years. People are afraid of it, as they feel acupuncture’s disadvantages make it difficult to try it. Yet it has health benefits, despite the pricking of needles.
Over the last few years, acupuncture has indeed shown a rise in popularity among healthcare providers as a viable form of treatment and helps treat conditions such as chronic back pain, headaches, and nausea after chemotherapy, among several others.
There are several misconceptions about acupuncture, but nevertheless, the truth is that it does provide relief to people all over the world.
The most common myths viewed as acupuncture disadvantages
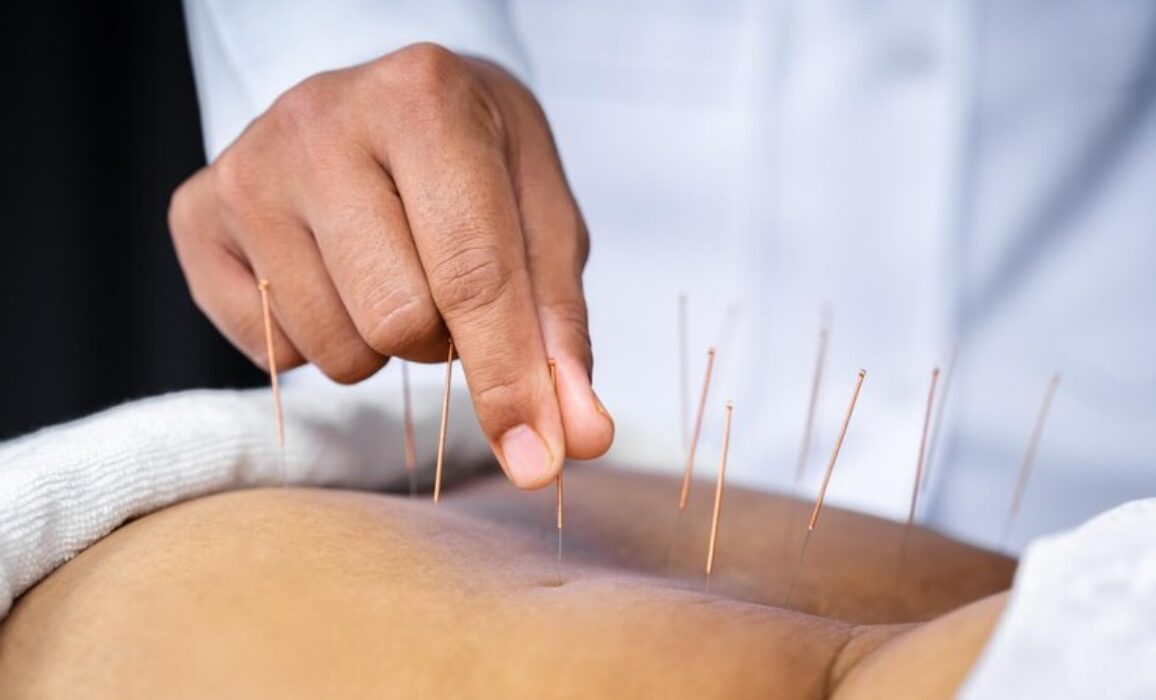
Myth 1: Acupuncture hurts—use of acupuncture needles
Perhaps the thought of being pricked by several needles at once makes a person shiver. It is a common reaction. But it does not have to be so. There is very minimal discomfort with acupuncture, as the needles used are very fine and thin, about the size of a cat’s whisker.
Any sort of discomfort will either fade on its own or ease up as the acupuncturist adjusts the needles.
Myth 2: Acupuncture is an ancient folk medicine, and no legitimate healthcare professional will recommend it.
It is true that acupuncture is ancient. However, it is a treatment option that several medical institutions recommend. There are several clinical research trials on acupuncture. Both the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the World Health Organization (WHO) recognize acupuncture as a valid treatment for a wide range of conditions.
Acupuncture is no doubt used by a diverse patient population, from very young to very old. People look into the long-term benefits of acupuncture.
Myth 3: Acupuncture may conflict with medication, physical therapy, and medical treatments.
Acupuncture can indeed be performed alongside conventional therapeutics; with a few exceptions, it is understood. Caution needs to be exercised when taking blood thinners.
“In cases where the patient is on blood thinners, smaller needles are used. According to a specialist, there is a very minor increase in the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Myth 4: Acupuncture is only useful for treating pain.
• It is true that acupuncture can help relieve pain. But it is also used for a wide range of treatments for other health issues, like:
• Knee pain.
• Back pain.
• Headache.
• Nausea and vomiting.
• Stomach pain.
• Menstrual cramps.
• Chemotherapy side effects.
• Morning sickness.
• Allergies.
• High blood pressure.
• Depression.
• Infertility.
Myth 5: Acupuncture has lots of side effects. More time off from work
Acupuncture has indeed few to no side effects.
Myth 6: Once acupuncture begins, the person always needs acupuncture.
The response to acupuncture is always, of course, an individual one. Few people with acute and minor issues respond quickly, within one, two, or three treatments. Others need a course of eight to 10 treatments to see proper improvement. Such an acupuncture disadvantage appears to be a myth, alright?
Myth 7: The person needs a doctor’s referral or a prescription for acupuncture.
It is understood that most patients need a doctor’s referral, and this is not so. Yet many people learn about acupuncture from their doctor. Few come to know via word-of-mouth.
Conclusion
Keeping aside the disadvantages of acupuncture, it is good to follow the necessary guidelines. At times, there is no need for a doctor’s referral or prescription for acupuncture, but a physician needs to perform a diagnostic exam for the condition that needs to be treated. It is, of course, important to consult a qualified and licensed acupuncturist prior to starting any course of treatment.